Is the renal pyramidal thickness a good predictor for pyeloplasty in postnatal hydronephrosis?
Amr Hodhod, MSC1, jean_paul Capolicchio, M.D1, Roman Jednak, M.D1, Abd-Elalim ElDoray, PhD2, Tarek Abd El-bakey, PhD3, Mohamed El-sherbiny, PhD1.
1Mcgill University health center, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2Menoufia faculty of medicine, Shebin Elkom, Egypt, 3Menoufia faculty of medicine, Shebin El-Kom, Egypt.
Abstract
Background
However, in addition to its subjectivity, the parenchymal thickness essentially changed with age that makes its clinical application difficult especially in bilateral hydronephrosis.1 The pyramidal thickness changes little over the first nine years of life that makes it superior to the parenchymal thickness.1
We tried to prove the feasibility of PT measurement in hydronephrosis. Furthermore, We postulated that a definite PT might predict pyeloplasty. So, we tried to evaluate PT as a predictor for pyeloplasty in comparison with other possible predictors like APD, SFU grading, and renogram findings.
Patients and methods:
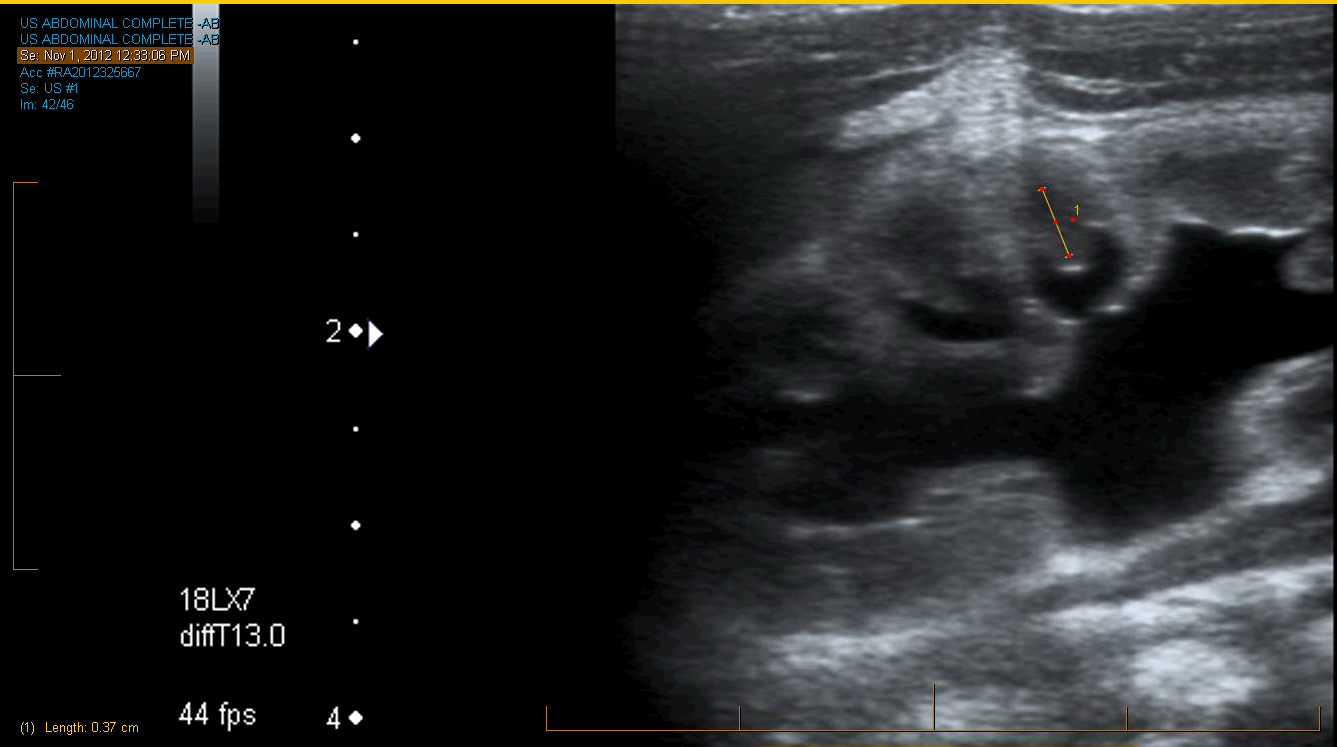
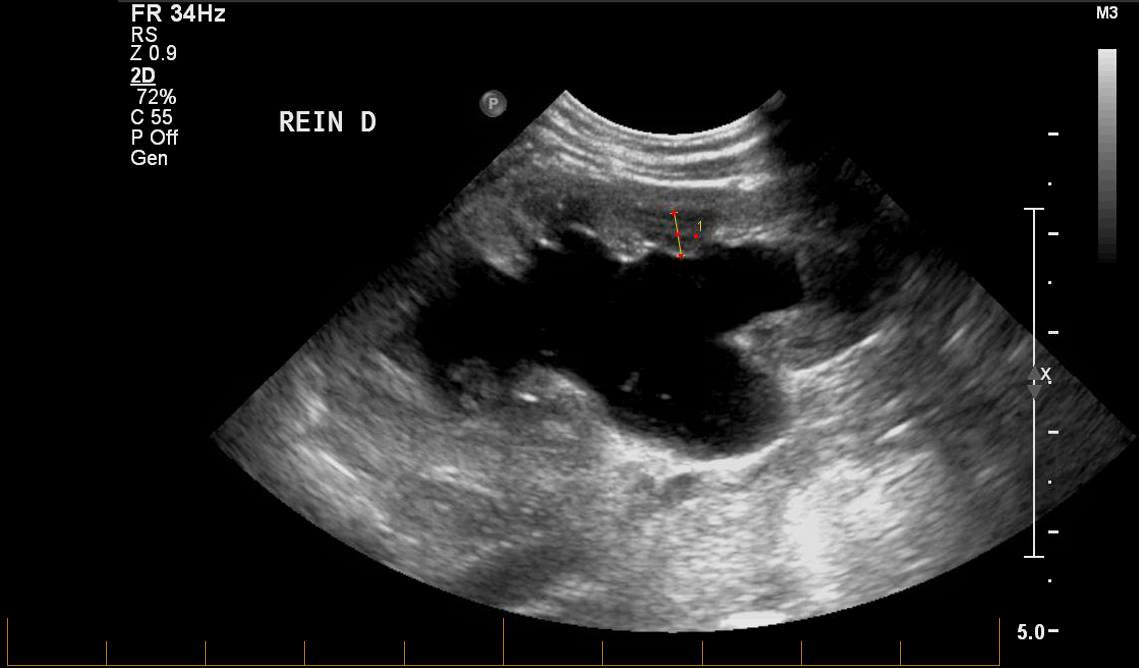
We retrospectively reviewed patients’ charts who presented with postnatal hydronephrosis from 2008 to 2013. Included cases had grade 3 or 4 hydronephrosis. We included only units diagnosed as uretero-pelvic junction obstruction. Gender, laterality, hydronephrosis side, renogram data, and follow-up data were recorded. We reviewed all patients’ ultrasounds images. We measured PT and pelvic antero-posterior diameter (APD) in the last ultrasound before surgery otherwise were measured in the ultrasound with worst hydronephrosis. PT was measured in supine position in the middle1/3 of the sagittal renal plane. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to correlate the collected parameters to pyeloplasty incidence. Receiver operating characteristic curve was used to evaluate the cutoff value of PT that predicts pyeloplasty. Post-pyeloplasty PT change (ΔPT) was evaluated and compared to the postoperative hydronephrosis status.
Results:
Total included cases were 155 patients (165 units). 114 units had grade 3 hydronephrosis and 51 units had grade 4 hydronephrosis. 50 cases (53 units) underwent pyeloplasty. The median follow-up period was 26.3 months. Univariate analysis revealed that SFU grading, APD, PT, T1/2 and MAG-3 curves were associated with surgery. Multivariate analysis showed that PT and renogram curve were independent predictors for surgery. PT ≤ 3mm had 98.2 % sensitivity and 85.5% specificity in predicting pyeloplasty. ΔPT was significantly associated with post-pyeloplasty hydronephrosis improvement (p<0.016).
Conclusion:
PT measurement is feasible in hydronephrosis. PT ≤3mm can predict pyeloplasty and ΔPT is significantly associated with post-pyeloplasty improvement of high-grade hydronephrosis.
References:
1 Kadioglu A. Renal measurements, including length, parenchymal thickness, and medullary pyramid thickness, in healthy children: what are the normative ultrasound values? AJR Am J Roentgenol 2010; 194(2): 509-15.
Figure Measurement of the renal pyramidal thickness in various hydronephrosis modules
Table 2 Univariate and multivariate COX- regression analyses regarding pyeloplasty
| Parameters | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
| Hazard ratio (confidence interval) | P value | Hazard ratio (confidence interval) | P value | |||
| Gender | 0.992 (0.675- 1.261) | 0.613 | --------- | |||
| Laterality | 1.481 (0.837-0.837) | 0.178 | --------- | |||
| SFU | Grade 3 | 0.240 (0.137-0.137) | <0.001 | 1.342 (0.652-2.759) | 1.342 | |
| Grade 4 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| PT | 0.566 (0.479-0.670) | <0.001 | 0.593 (0.446-0.789) | <0.001 | ||
| APD | 1.055 (1.035-1.075) | <0.001 | 1.001(0.966-1.039) | 0.914 | ||
| MAG-3 | T1/2 | 1.003 (1.001- 1.006) | 0.012 | 0.999 (0.995-1.003) | 0.826 | |
| DRF | 0.996 (0.980-1.013) | 0.655 | ----------- | |||
| Curve | Obstructive | 1 | <0.001 | 1 | 0.006 | |
| Non-obstructive | 0.102 (0.041-0.257) | 0.246 (0.09-0.674) | ||||
Figure 2 ROC curve demonstrates the relationship of the pyramidal thickness regarding the surgical interference

Back to 2016 Fall Congress
