The Presence of Cultivatable Bacteria in the Bladders of Children: When Does a Pediatric Urinary Microbiome Begin?
Thomas Halverson, MS1, Douglas Storm, MD2, Hillary Copp, MD3, Denise Juhr, MS2, Zachery Kornberg, MS3, Alan Wolfe, PhD1.
1Loyola University, Chicago, IL, USA, 2University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, Iowa City, IA, USA, 3University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, USA.
BACKGROUND: Bacterial communities (microbiota) in the urinary bladder along with associations between bladder microbiota profiles and lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) have been reported in adults. However, it is not yet known when the bladder microbiota becomes established. The purpose of this study was to determine when the bladder microbiota is established and compare pediatric microbiota profiles of several urogenital sites.
METHODS: With IRB approval, 31 children ≤ 18 years without antibiotic exposure in prior 3 months were recruited from 2 institutions. The following samples were collected: transurethral catheter urine (TUC), perineal skin swab (PSS), urethral skin swab (USS), vaginal skin swab (VSS), and foreskin swab (FS). The specimens were assessed using the expanded quantitative urine culture (EQUC) protocol, designed to detect bacteria and yeast found in pelvic floor samples. Bacteria were identified via MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. Specimens also were assessed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing.
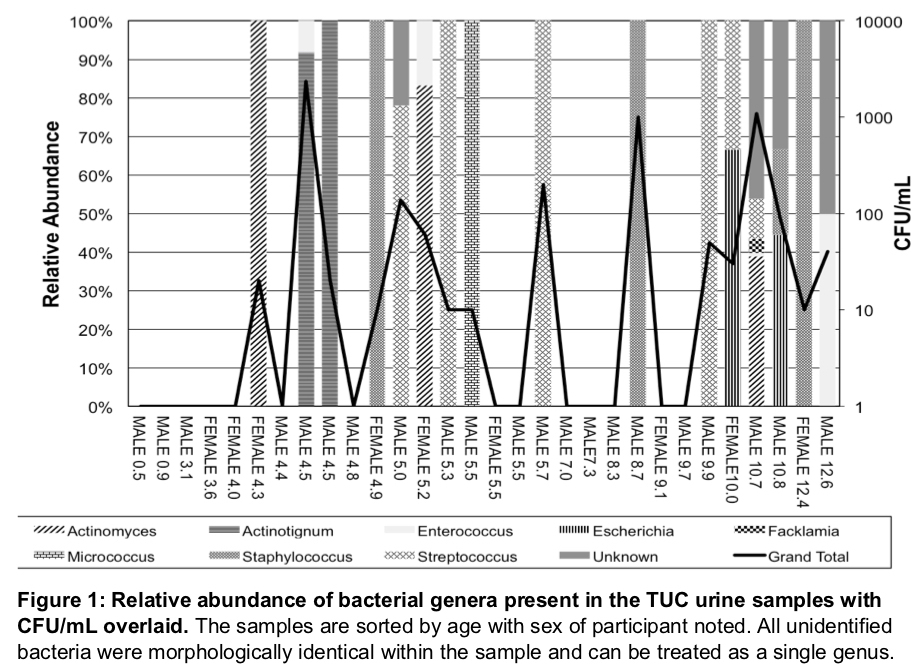
RESULTS: The 31 participants included 21 males and 10 females, median age 5.5 years, range 5 weeks-12.6 years. Bacterial microbiota was detected beginning at 4 years of age. EQUAC-positive TUC samples were present in 11 of 21 (52%) males and 5 of 10 (50%) females. 19 of the 28 (68%) USS samples were EQUC-positive. 24 of 28 (86%) PSS samples were EQUC-positive. 6 of 7 (86%) FS samples were EQUC-positive. 8 of 10 (80%) VSS samples were EQUC-positive. The TUC microbiota were low biomass (0-2340 CFU/mL; median of all TUC samples, 10 CFU/mL; median of TUC-positive samples only, 40 CFU/mL). Most were composed of one genus (56%); only 2 EQUC-positive samples were composed of ≥2 genera (12.5%). No relationship was observed between presence or abundance of cultivated microbes and participant age (Figure 1). The currently analyzed sequence data generally concurs with the EQUC data, but detects genera not detected by EQUC.
CONCLUSIONS: Cultivatable microbes can be detected in the bladders of ~50% of children as early as 4 years of age. Often, the TUC samples were low biomass and featured one genus. Additional sample collection is ongoing to further delineate earliest establishment of urinary microbiota.
Back to 2019 Abstracts




