Prune Belly Syndrome (PBS) - evidence for a gestational gene-environment interaction
Nathalia G. Amado, PhD1, Thomas J. Egeland, MS2, Sujay S. Ithychanda, PhD3, Nixon Raj, PhD1, Justin J. Wobser, MS1, Nida S. Iqbal, PhD2, Alexandria N. Fusco, BA2, Ashley Jackson, PhD1, Jun Qin, PhD3, Roy Zent, MD/PhD4, Linda A. Baker, MD1.
1Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH, USA, 2University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA, 3Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH, USA, 4Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA.
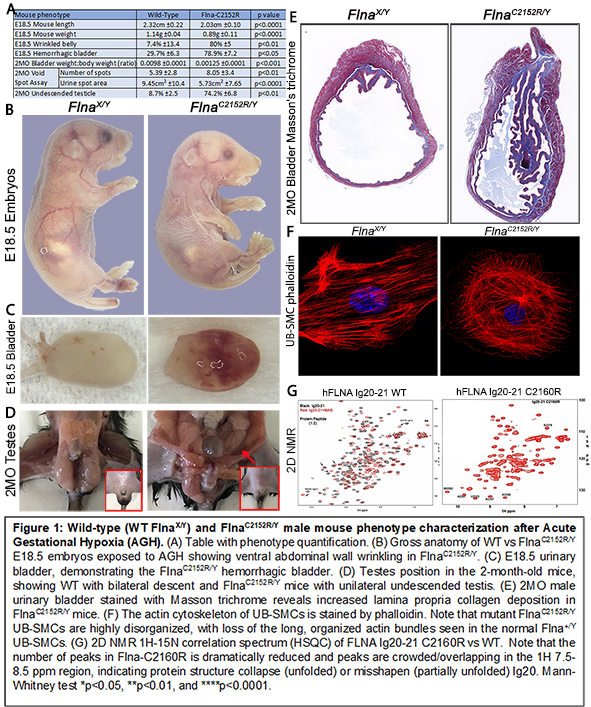
BACKGROUND: PBS is an ultrarare, mild to lethal human multiple congenital anomaly complex. We identified 4 humans with pathogenic FLNA missense mutations, including the severe FLNA p.C2160R gain-of-function mutation. The X-linked FLNA gene encodes a smooth muscle cell (SMC) regulatory mechano-sensing actin-crosslinking cytoplasmic protein that transmits force bidirectionally between actin and integrins, binds hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, and translocates to the nucleus to activate hypoxic gene regulation. The p.C2160R mutation resides within the critical regulatory immunoglobulin-like (Ig) repeat 20 that harbors an autoinhibitory binding site for β1 integrins. To reveal mechanistic causality, we 1) created the analogous Flna-C2152R mice using Crispr-Cas9 and assessed the effect of gestational hypoxia, and 2) studied the mutationís impact on ligand binding by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).
Methods: Homozygous FlnaC2152R/C2152R dams were timed-mated to hemizygous FlnaC2152R/Y mice. The pregnant dams were exposed to acute gestational hypoxia (AGH) (8hrs of 6% O2 at embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5)) and then returned to normoxia. The male offspring (AGH FlnaC2152R/Y mice) were assessed at E18.5 and adult 2-months old (2MO) for gross morphology, bladder organ function, histology, and molecular phenotypes by qPCR. 2MO mice underwent bladder function 4-hour voiding spot assay (VSA), quantifying the number and area of urine spots on filter paper. Urinary bladder SMC were isolated from AGH FlnaC2152R/Y and cell morphology, spreading and adhesion were analyzed. WT and mutant Flna Ig19-21 protein domains were evaluated for binding to MAS ligand by NMR spectroscopy.
Results: When compared to WT mouse AGH controls, FlnaC2152R/Y AGH mice manifested abdominal wall laxity, hemorrhagic, dysfunctional, fibrotic, dilated urinary bladder, and intra-abdominal undescended testes in 80%, 78%, and 74% of mice, respectively (Fig1A-D). Also, the AGH FlnaC2152R/Y mice had extra genitourinary abnormalities including abnormal spine curvature and bell-shaped rib cage (data not shown, DNS). Histologically, the FlnaC2152R/Y bladders showed a thicker detrusor SMC layer with increased collagen deposition (Fig1E). By qPCR, E18.5 and 2MO bladder had reduced expression of SMC markers (Myocardin, Myh11, Transgelin, and Cnn1) (DNS). VSA revealed increased number of urine spots with reduced spot area consistent with frequent, small voids (dysfunctional voiding) in FlnaC2152R/Y AGH mice (Fig1A). The mouse-derived FlnaC2152R/Y bladder SMC are dysmorphic, with altered actin stress fiber formation, cell spreading, and focal adhesion (Fig.1F and DNS). NMR-based protein domain structural analysis revealed the human C2160R mutation led to Ig20 domain misfolding, Ig21 autoinhibition disruption, and enhanced FLNA MAS/β1 integrin ligand binding (Fig1G). Conclusions: Human missense mutations in the X-linked FLNA gene can cause PBS. The FLNA p.C2160R gain-of-function mutation leads to profound Ig20 domain dysfunction and overall dysregulation of the integrin-filamin A-actin network as shown by the highly penetrant PBS-like phenotype in the FlnaC2152R/Y AGH male mice. The collective findings of these studies of gestational gene-environment interaction provide mechanistic causality at the organ, cellular, and molecular levels. NIH-DK100483, DK127589 PI:Baker AUA/UCF Research Scholar Award PI:Amado
Back to 2023 Abstracts
